This blog post is aimed to express and explain my surprise about Signal being more secure than I thought (due to receipt acknowledgments). I hope you find it interesting, too.
Signal, and especially its state update protocol, the Double Ratchet algorithm, are widely known for significantly increasing security for instant messaging. While most users first see the end-to-end security induced by employing Signal in messaging apps, the properties achieved due to
ratcheting go far beyond protecting communication against (active) attackers on the wire. Due to updating the local device secrets via the Double Ratchet algorithm, the protocol ensures that attackers, who temporarily obtain a device's local storage (on which Signal runs), only compromise confidentiality of parts of the communications with this device. Thus, the leakage of local secrets from a device only affects security of a short frame of communication. The exact duration of compromise depends on the messaging pattern among the communicating parties (i.e., who sends and receives when), as the state update is conducted during the sending and receiving of payload messages.
The Double Ratchet
The Double Ratchet algorithm consists of two different update mechanisms: the symmetric ratchet and the asymmetric ratchet. The former updates symmetric key material by hashing and then overwriting it with the hash output (i.e.,
k:=H(
k)). Thus, an attacker, obtaining key material can only predict future versions of the state but, due to the one-wayness of the hash function, cannot recover past states. The asymmetric ratchet consists of Diffie-Hellman key exchanges (DHKE). If, during the communication, party A receives a new DH share
gb as part of a message from the communication partner B, then A samples a new DH exponent
a and responds with the respective DH share
ga in the next sent message. On receipt of this DH share, B will again sample a new DH exponent
b' and attach the DH share
gb' to the next message to A. With every new DH share, a new DHKE
gab is computed among A and B and mixed into the key material (i.e.,
k:=H(
k,
gab)). For clarity, I leave out a lot of details and accuracy.
As new DH shares
ga and
gb are generated from randomly sampled DH exponents
a and
b, and the computation of
gab is hard if neither
a nor
b are known, the key material recovers from an exposure of the local secrets to an attacker after a new value
gab was freshly established and mixed into it. Summing up this mechanism, if an attacker obtains the local state of a Signal client, then this attacker cannot recover any previously received message (if the message itself was not contained in the local state), nor can it read messages that are sent after a new
gab was established and mixed into the state. The latter case happens with every full round-trip among A and B (i.e., A receives from B, A sends to B, and A receives again from B).
 |
| Conceptual depiction of Double Ratchet in Signal two years ago (acknowledgments were only protected between client and server). The asymmetric ratchet fully updates the local secrets after one round-trip of payload messages. |
Research on Ratcheting
During the last two years, the Signal protocol inspired the academic research community: First, a formal security proof of Signal was conducted [1] and then
ratcheting was formalized as a generic primitive (independent of Signal) [2,3,4]. This formalization includes security definitions that are derived via 1. defining an attacker, 2. requiring security unless it is obvious that security cannot be reached. Protocols, meeting this
optimal notion of security, were less performant than the Double Ratchet algorithm [3,4]. However, it became evident that the Double Ratchet algorithm is not as secure as it could be (e.g., recovery from exposure could be achieved quicker than after a full round-trip; see, e.g., Appendix G of our paper [3]). Afterwards, protocols (for slightly weakened security notions) were proposed that are similarly performant as Signal but also a bit more secure [5,6,7].
Protecting Acknowledgments ...
In our analysis of instant messaging group chats [8] two years ago (blog posts: [9,10]), we found out that none of the group chat protocols (Signal, WhatsApp, Threema) actually achieves real recovery from an exposure (thus the asymmetric ratchet is not really effective in groups; a good motivation for the
MLS project) and that receipt acknowledgments were not integrity protected in Signal nor WhatsApp. The latter issue allowed an attacker to drop payload messages in transmission and forge receipt acknowledgments to the sender such that the sender falsely thinks the message was received. Signal quickly reacted on our report by treating acknowledgments as normal payload messages: they are now authenticated(-encrypted) using the Double Ratchet algorithm.
... Supports Asymmetric Ratchet
Two years after our analysis, I recently looked into the Signal code again. For a training on ratcheting I wanted to create an exercise for which the lines in the code should be found that execute the symmetric and the asymmetric ratchet respectively. Somehow I observed that the pure symmetric ratchet (only updates via hash functions) was nearly never executed (especially not when I expected it) when lively debugging the app but almost always new DH shares were sent or received. I realized that, due to encrypting the receipt acknowledgments now, the app always conducts full round-trips with every payload message. In order to observe the symmetric ratchet, I needed to temporarily turn on the flight mode on my phone such that acknowledgments are not immediately returned.
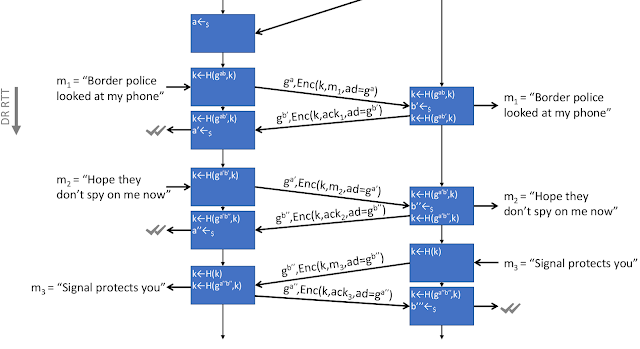 |
| Conceptual depiction of Double Ratchet in Signal now (acknowledgments encrypted). The asymmetric ratchet fully updates the local secrets after an acknowledgment for a message is received. |
Consequently, Signal conducts a full DHKE on every sent payload message (in case the receiving device is not offline) and mixes the result into the state. However, a new DH exponent is always already sampled on the previous receipt (see sketch of protocol above). Thus, the exponent for computing a DHKE maybe remained in the local device state for a while. In order to fully update the state's key material, two round-trips must be initiated by sending two payload messages and receiving the resulting two acknowledgments. Please note that not only the mandatory receipt acknowledgments are encrypted but also notifications on typing and reading a message.
If you didn't understand exactly what that means, here a tl;dr: If an attacker obtains your local device state, then with Signal all previous messages stay secure and (if the attacker does not immediately use these secrets to actively manipulate future conversations) all future messages are secure after you wrote two messages (and received receipt acknowledgments) in all of your conversations. Even though this is very (in practice certainly sufficiently) secure, recent protocols provide stronger security (as mentioned above) and it remains an interesting research goal to increase their performance.
[1]
https://eprint.iacr.org/2016/1013.pdf [2]
https://eprint.iacr.org/2016/1028.pdf [3]
https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/296.pdf [4]
https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/553.pdf [5]
https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/889.pdf [6]
https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/954.pdf [7]
https://eprint.iacr.org/2018/1037.pdf [8]
https://eprint.iacr.org/2017/713.pdf [9]
https://web-in-security.blogspot.com/2017/07/insecurities-of-whatsapps-signals-and.html [10]
https://web-in-security.blogspot.com/2018/01/group-instant-messaging-why-baming.html



